AI Against Crime:
Pioneering Innovations that Transform the Fight Against Crime
Estimated Reading Time: Approximately 20 minutes.
For the anti-fraud, AML, cyber security, and Law Enforcement communities.
What You Will Learn:
- The role of graph, AI and ML in revolutionizing crime prevention and detection
- The landscape of advanced AI techniques including Graph AI
- Real-world examples of AI applications in fighting crimes
- Examples of useful AI applications, services, and software
In an era marked by digital advances and rising illicit activities, the anti-crime community faces unique challenges. Traditional crime-fighting strategies are enhanced by innovative technologies to tackle modern criminal activities. The advent of generative AI has shifted our interaction with AI from passive to active, offering new tools that improve crime-fighting capabilities. However, these technological benefits also bring vulnerabilities, as criminals can exploit these advancements. Regulatory frameworks are vital, covering tool usage, application methods, and their legal admissibility, alongside concerns about data privacy, especially with AI tools often provided as cloud-based services due to their high computational demands.
Graph, AI and Machine Learning (ML) have become crucial in crime detection and prevention. They excel at identifying patterns within large datasets, a task daunting for human analysts. For example, in financial fraud detection, AI can analyze millions of transactions to find fraudulent ones, a task comparable to finding a needle in a constantly growing haystack.
Integrating AI and ML with graph analytics reveals hidden connections within your data, offering new insights for detection mechanisms and generative AI making those more precise and accurate. Generative AI, for example, enhances analysts' abilities in significant ways. Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT bring innovative approaches to interpreting complex documents and summarizing vast amounts of information, aiding analysts buried under data by providing concise summaries and highlighting critical findings, thus streamlining the review process.
This paper explores the impact of AI, ML, and graph technologies on crime fighting. It presents real-life examples and explanations to demonstrate how these innovations are integrated into crime-fighting strategies and serve as investigative and preventive tools. It envisions a future where the full potential of GenAI and AI analytics is harnessed to protect communities against digital-age criminal threats.
Get This Paper

Experience the Power of the DataWalk Platform in Action
AI Framework in Crime Prevention and Investigation
In general, Graph AI brings together a variety of key graph and AI-based functions for integrating, organizing, understanding, and analyzing complex interconnected data. The integration of graph and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies in crime prevention and investigation has become a cornerstone for the anti-crime community, offering advanced tools to enhance the effectiveness of law enforcement and intelligence efforts. The categorization of AI technologies, as proposed by the IT consulting giant Gartner, provides a valuable framework for understanding and applying these innovations in the field. This perspective outlines various AI technologies and their potential applications, emphasizing the multifaceted approach required to address contemporary criminal challenges.
- Perception Systems: Key technologies like Computer Vision and Auditory systems are central to modern surveillance and monitoring strategies. For example, Computer Vision plays a crucial role in facial recognition technologies and object detection solutions such as gun, drug, or nudity detection, by significantly bolstering efforts to identify individuals or objects of interest and improve overall public safety.
- Probabilistic Reasoning: This category, encompassing Machine Learning, predictive modeling, and deep learning, among others, is instrumental in crime prediction and prevention. Predictive policing tools leverage these technologies to analyze historical crime data and forecast potential future incidents, allowing law enforcement to allocate resources more strategically. Machine learning algorithms are also employed in the financial, health, e-commerce, retail, telco, and manufacturing ecosystems to detect patterns indicative of fraudulent transactions, suspicious contractors, suspicious claims, and other suspicious activities.
- Computational Logic: Rule-Based Detection Engines: Leveraging computational logic, these engines employ rule-based algorithms and logical inference to automate the detection of criminal patterns, drawing on human expertise and experience.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): spans text analytics, understanding, generation, and more, enabling machines to process human language in tools like ChatGPT for dialogues and summarization. Feeding these tools via a knowledge graph enables results that are more domain-oriented and more precise. It's pivotal for sentiment analysis, allowing organizations to gauge public opinions efficiently. NLP's real power lies in converting unstructured data into a structured form, crucial for deep analysis. Techniques like Named Entity Recognition (NER) help identify and categorize essential data elements, such as names and locations, from vast text volumes, streamlining data preparation and speeding up investigations for the law enforcement and intelligence sectors.
- Knowledge Representation, Learning and Search: This Graph AI category reflects the intertwined nature of organizing complex information and efficiently navigating vast datasets. Knowledge Representation, through technologies like Knowledge Graphs and Semantic Networks, offers deep insights into the networks and relationships within criminal organizations. Coupled with advanced Learning and Search algorithms, analysts can swiftly sift through criminal databases and digital evidence, extracting relevant information with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This combined approach is essential for understanding the complexities of criminal networks and formulating informed strategies for investigation and prevention.
Figure 1: The screen below presents an example from DataWalk’s Graph AI platform, showcasing a knowledge graph that facilitates the representation of organizational or agency knowledge by organizing data around business objects and their interconnections. This knowledge graph enables further analysis through features such as no-code querying, scoring, and link chart investigations, enhancing the ability to derive insights and make informed decisions.
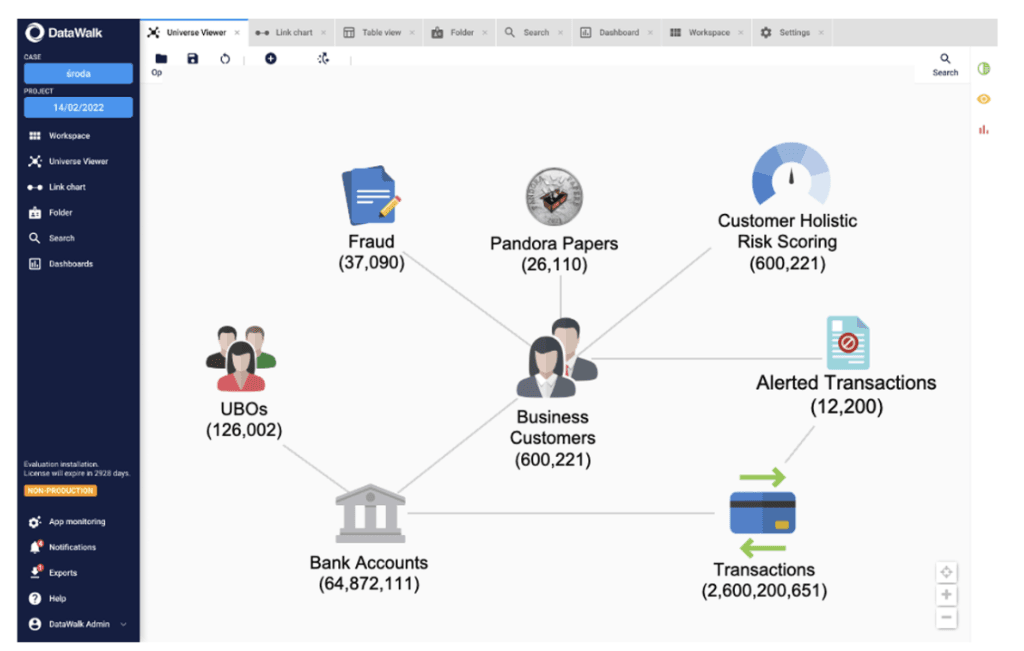
The AI framework described above serves as a comprehensive guide for the anti-crime community, highlighting the diverse applications of AI technologies in the fight against crime. By leveraging these categories, law enforcement, intelligence agencies, and crime analysts are equipped to tackle the evolving landscape of criminal activity, ensuring a safer and more secure society in an increasingly digital age.
Practical examples of using AI for combating crimes
While Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers many theoretical benefits, its true value emerges only through its application to real-world scenarios within the crime-fighting arena. Without practical implementation, AI remains a mere technological possibility rather than a transformative tool. By integrating AI technologies into everyday intelligence workflows, the anti-crime community can unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and depth in their operations. Here are several practical examples that illustrate how AI is being effectively applied to combat crime and enhance public safety:
- Explaining complex concepts
ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLMs) are instrumental in deciphering complex topics within the anti-crime domain, particularly useful for understanding the intricacies of cryptocurrency transactions which are often exploited in financial crimes. These models can simplify the concepts of blockchain technology, trace the flow of digital currencies, and explain the methods used in cyber laundering, thereby aiding law enforcement agencies in their investigative and educational efforts. Additionally, LLMs can be utilized to clarify legal jargon, cybercrime statutes, and digital forensic techniques, enhancing the skill set of professionals combating crime.
Note: ChatGPT requires an internet connection, as data and prompts must be transmitted to OpenAI's cloud servers (through the ChatGPT interface or API). Therefore, it's important to be mindful of the information you share with ChatGPT. On the other hand, alternative open-source offline models, such as LLaMA 2, Mistral 7B, Falcon, and others, are available. However, their effectiveness can vary significantly depending on the task, and they may require substantial infrastructure costs.
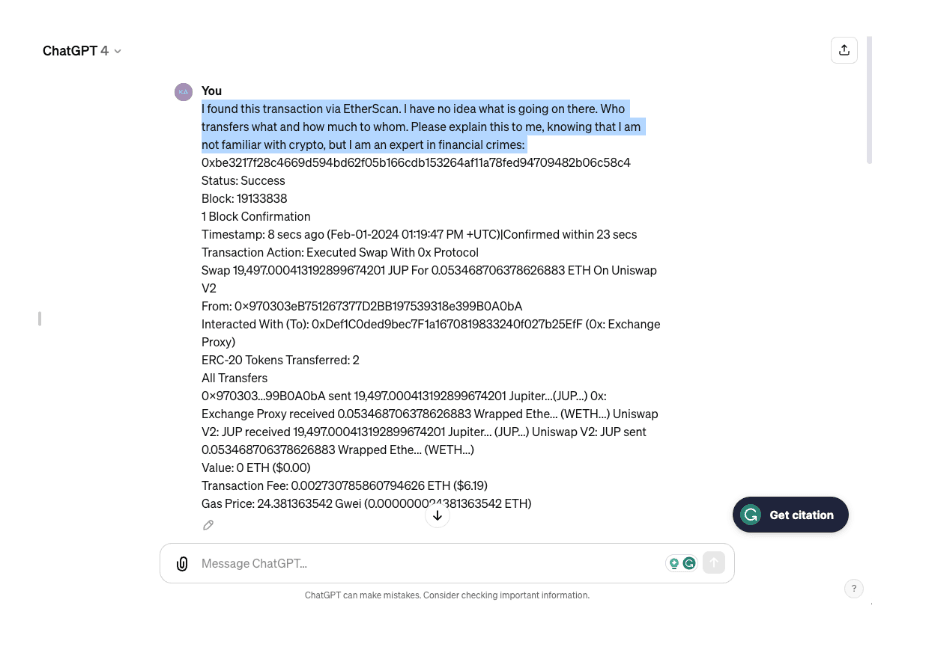
Figure 2: This example illustrates how one of the large law enforcement agencies uses ChatGPT to explain complex cryptocurrency transfers downloaded from Etherscan.io.

- Support in data preparation
ChatGPT, with its advanced capabilities, is a potent tool for analysts and investigators. It facilitates the acquisition of new skills, such as coding, and streamlines complex analytical tasks. By interacting with ChatGPT, individuals can use programming languages without knowing how to program. This newfound proficiency can significantly enhance their investigative capabilities, allowing for more sophisticated approaches to data analysis and problem-solving.
Note: It may be necessary to reiterate prompts since large language models (LLMs) can sometimes produce inaccurate or incorrect responses and are less deterministic than other rule-based systems.
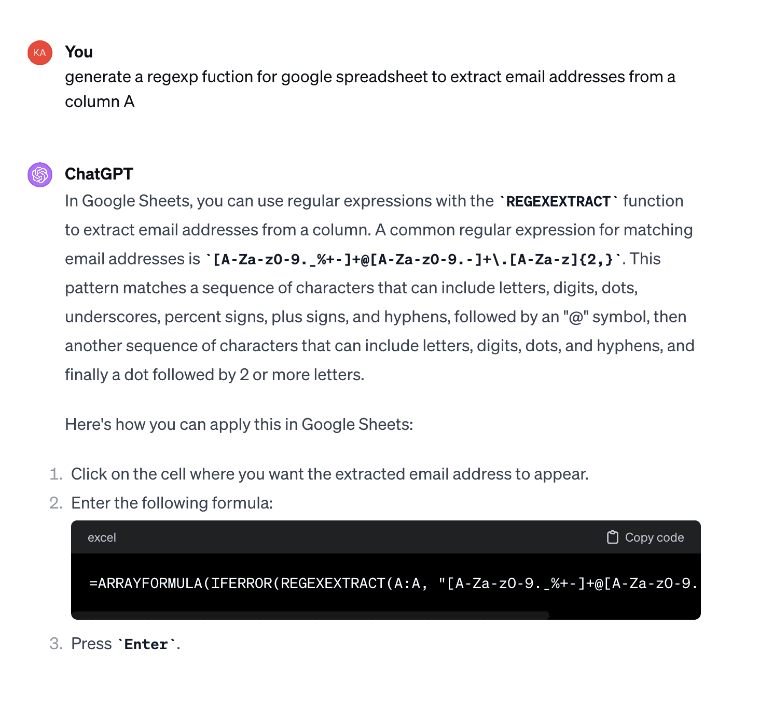
Figure 3. This screenshot illustrates an interaction where analysts are prompted to create a regular expression function in Google Sheets to automate the extraction of email addresses from text messages. The example showcases the potential of ChatGPT in streamlining analytical tasks.
Furthermore, the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, particularly entity extraction, revolutionizes the way information is processed from textual data. NLP can automatically identify and extract relevant entities, such as names, places, and organizations, from vast amounts of unstructured text. This capability is invaluable in investigations, where sifting through extensive documentation manually would be time-consuming and prone to oversight. By leveraging NLP, analysts can quickly gather critical information, track connections, and uncover patterns, thereby accelerating the investigative process and enhancing the overall accuracy of their findings.
- Enhanced trend detection
Serious crimes are often structured and organized, requiring financial institutions to understand their customers' behaviors over time rather than merely focusing on single outliers. For such comprehensive trend analysis, machine learning proves invaluable, offering insights into customer profiles, their evolving behaviors, and any permanent, anomalous changes compared to similar customers. This technique, pivotal for KYC analyses, extends beyond customers to suppliers, contractors, agents, patients, doctors, and more, providing a broad spectrum of applications for robust risk management.
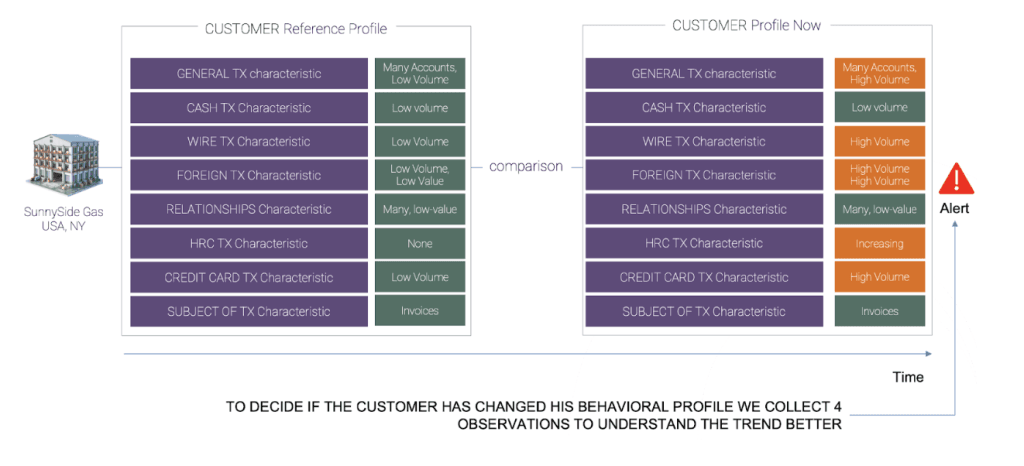
Figure 4. The picture below illustrates the DataWalk AI methodology (machine learning - unsupervised learning) employed by a large European bank to define entity reference profiles, which are composed of diverse attributes such as characteristics of cash transactions, relationship transactions, and foreign transactions. The significance of these characteristics is delineated through a business ontology with descriptors like "Low volume, High value," etc. The reference profile undergoes a comparative analysis against the entity's behavior across four subsequent observations to ascertain whether there have been any permanent changes in its characteristics or overall profile. To access the complete paper, please download it here.
- Fraud detection, monitoring, and crime prediction.
Today's criminal activities are increasingly complex and multifaceted, necessitating advanced and diverse approaches for effective detection and prevention. A combination of sophisticated algorithms and techniques is essential to navigate this intricate landscape. By integrating methods such as graph embeddings, which capture the intricate relationships within data, decision trees for clear, rule-based classification, and regression analysis to predict outcomes, we enhance our ability to uncover and understand criminal patterns. Additionally, graph algorithms like community detection play a crucial role in identifying hidden networks and relationships within data, enabling more effective monitoring and predicting of fraudulent activities. This holistic approach, leveraging a blend of advanced analytical tools, is key to staying ahead in the ongoing fight against sophisticated crime.
Figure 5. The figure illustrates the application of Graph Embedding techniques by a major bank using the DataWalk system to identify high-risk accounts. The system has effectively clustered accounts, pinpointing a significant group where 98.4% are deemed high-risk, while only a small fraction, 1.6%, are considered low-risk. Due to their connections within the cluster, the risk level for these low-risk accounts should be re-evaluated and potentially increased. Download the full paper.

- Resolve entities with greater accuracy
In enhancing the accuracy of entity resolution, various sophisticated techniques are employed beyond basic strict matching, incorporating advanced methodologies such as fuzzy matching to account for discrepancies and ambiguities in data. Algorithms like Eudex and Double Metaphone play a pivotal role in this context by phonetically analyzing and matching similar-sounding entities, even when spelled differently. Complementing these are AI-driven approaches like text embeddings, which capture the semantic context of words, enabling a deeper understanding of entity relationships. Further enriching this landscape are graph embeddings and network analysis, which delve into the intricate web of connections between entities, unveiling patterns and associations not immediately apparent. Large Language Models (LLMs) add another layer of sophistication, leveraging vast amounts of data to predict and infer entity linkages with remarkable precision, thereby significantly enhancing the accuracy of entity resolution processes.
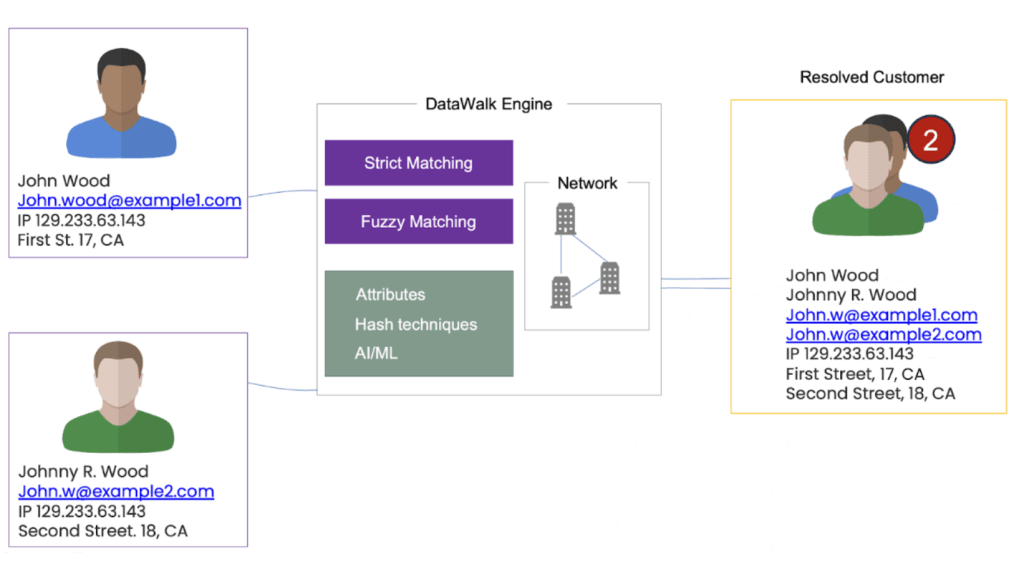
Figure 6. This diagram illustrates the process of entity resolution using the DataWalk engine. Two profiles for an individual named John Wood, with variations in contact details and addresses, are shown on the left. DataWalk applies strict and fuzzy matching techniques, along with attribute analysis using hash techniques, graphs and AI/ML, to reconcile these profiles. On the right, the outcomes are displayed as a "Resolved Customer" profile, which consolidates the individual's information into a singular entity, reflecting the engine's capability to identify and merge multiple records of the same entity.
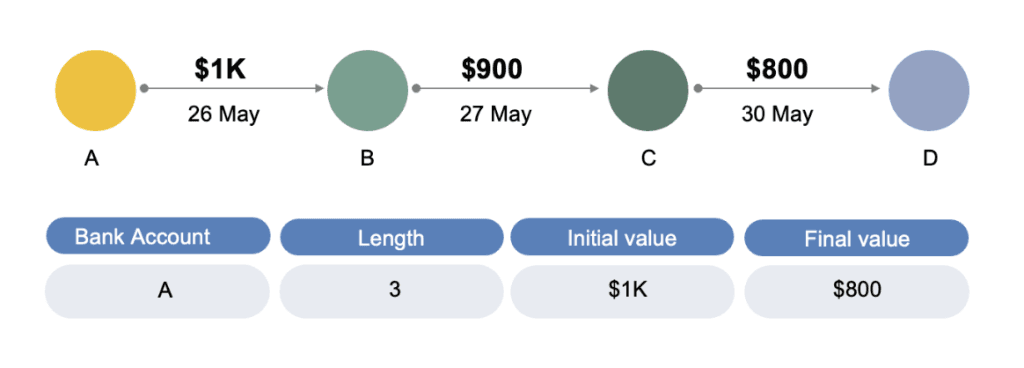
Identify suspicious transition chains in a “haystack”
Detecting Anti-Money Laundering (AML) layering within the vast sea of transactions is a formidable challenge for organizations, akin to finding a needle in a haystack, especially without a clear starting or endpoint. Traditionally, this task has been insurmountable for many, with attempts often ending in failure. However, by implementing enterprise knowledge graph concepts, this once-Sisyphean task becomes feasible. These graphs can sift through reams of data to uncover transaction patterns where subsequent amounts are lower than the preceding ones, forming a chain within a specific timeframe. This advancement marks a practical leap forward to identify and unravel the complex layers of AML schemes.
Figure 7. Sequential transactions flow within a specific period of time (a week), and the amount of each next transaction is close to X-10%
Note: Make sure that the Knowledge Graph (KG) technology you select can manage the data volume you possess. Not all KG solutions are crafted for handling operations of such complexity.
Make video and rich media infinitely more searchable
Agencies can harness AI tools to structure and make media and video content more searchable, eliminating the need for manual labor. These tools analyze elements like faces and objects, turning them into numerical data to understand content context. This AI-driven approach allows for quick retrieval of specific moments, saving countless hours that would otherwise be spent watching videos to locate relevant content.
- Combine various techniques to get better and more deterministic results
The fusion of techniques represents a significant leap forward in enhancing the reliability and interpretability of AI-generated insights. This integration is particularly crucial for making AI outputs more applicable in evidentiary and legal contexts, where the stakes are high and the demand for accuracy is paramount.
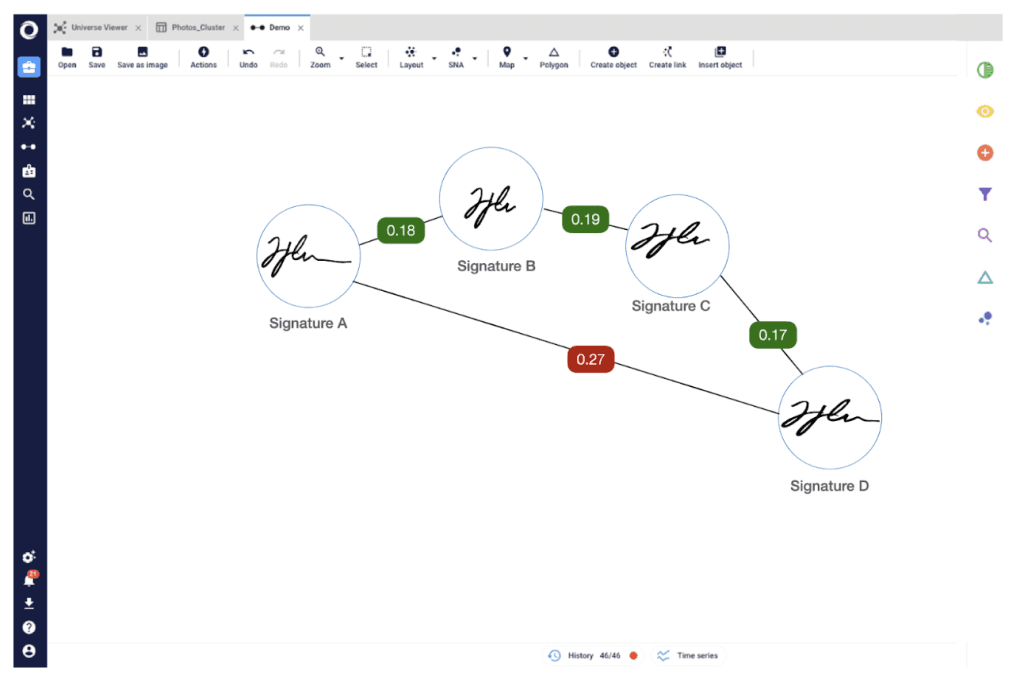
Knowledge graphs contribute a structured intelligence layer to the AI's processing capabilities, enabling a more nuanced understanding and connection between data points. For instance, in image analysis, AI might evaluate similarities based on predefined thresholds. Let's consider a scenario where AI is tasked with determining if a set of images are of the same subject. The AI is returns the list of pictures and their similarity rate. Analysts have to determine the threshold where pictures will be considered similar and different.
Figure 8. Using a similarity threshold of 0.2 as a standard for comparison. However, Signature A might be deemed similar to Signature B at a threshold of 0.18, and Signature B similar to Signature C at 0.19, and Signature C similar to Signature D at 0.17. The direct comparison between Picture A and Picture D might fall outside this range at 0.27, leading to a potential oversight by the AI. Here, a knowledge graph can bridge the gap by inferring that if A is similar to B and B is similar to C, C to D, then A should also be similar to C, ignoring the fact that the range is 0.27.
Another application of integrating LLMs with knowledge graphs is in document analysis and summarization, a task of particular relevance to intelligence agencies and units dealing with extensive volumes of data. For example, an intelligence agency might deploy an offline LLM to summarize and extract key findings from a large number of documents. Underpinning this LLM with a knowledge graph not only enhances the summarization process but also ensures that the outcomes are more deterministic. The knowledge graph aids in contextualizing the information, drawing connections between entities and events mentioned across documents, and refining the LLM's outputs to align with established facts and relationships. This results in summaries and insights that are not only concise but also enriched with a deeper level of understanding and relevance to ongoing investigations.
Figure 9. DataWalk ChatBot interface powered by the knowledge graph that can be integrated with LLM APIs or can incorporate an offline version of the open-source models.
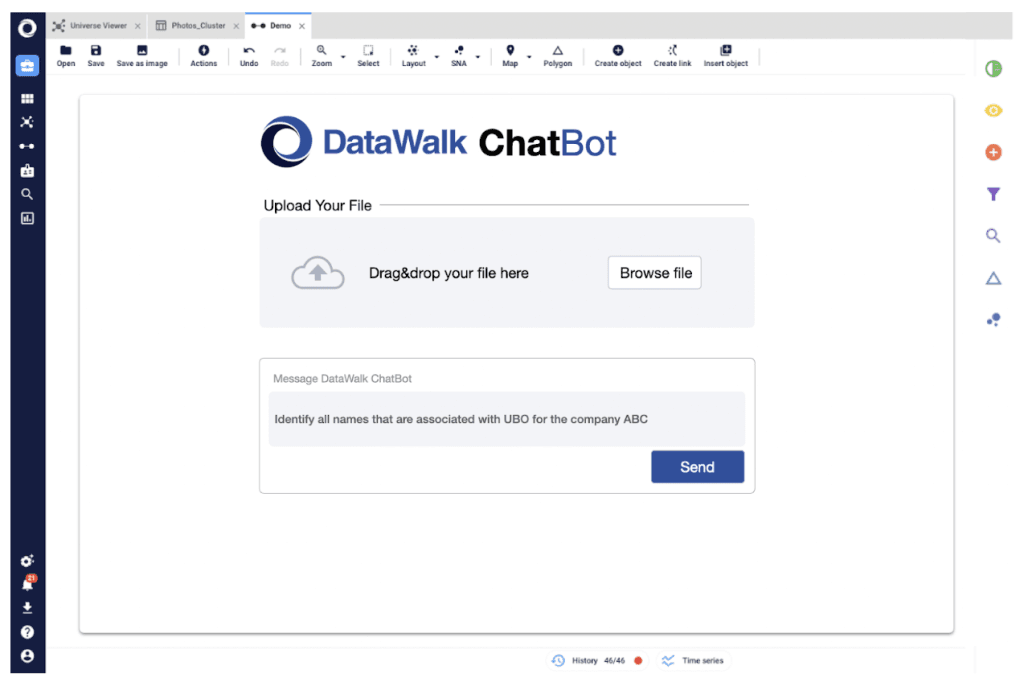
Figure 10. Prototype of DataWalk summary interface powered by the knowledge graph and LLMs that summarizes and explains contextual information gained from the knowledge graph on a single pane of glass. Super analysts can create their own AI assistants for various analytical tasks to automate, simplify, and accelerate analysis and investigation.

In crime-fighting, the strategic application of AI techniques and technologies emerges as a game-changer, significantly enhancing the capabilities of analysts. The key lies in identifying the core challenges and judiciously selecting the appropriate tools and methods to augment intelligence and improve performance. Analysts can dramatically increase their efficiency and effectiveness in combating crime by focusing on the most pertinent issues and leveraging the right AI solutions.
Appendix: Examples of commercial and enterprise-class AI solutions >>>
About DataWalk
DataWalk is a graph AI analytics platform designed to tackle crimes by merging graph-based and AI-driven methods to bolster fraud detection, combat money laundering, and expedite investigations. It sifts through extensive datasets to uncover intricate patterns and hidden connections, thereby streamlining the identification and action against crimes. This tool is pivotal in crime-fighting, offering deep insights and swift solutions through the fusion of graph analytics and AI. DataWalk stands out for its agility and seamless prototyping, catering to the fast-paced demands of crime-fighting analytics. Its rapid adaptability and user-friendly design allow for the swift development and testing of new data models and analytic strategies, ensuring law enforcement remains ahead of criminal innovations. With its capability to effortlessly assimilate fresh data sources and deploy leading-edge technologies, DataWalk enables continuous innovation and enhancement of investigative processes, making it an indispensable asset in crime prevention and investigation.
Solutions
Product
Partners
Company
Resources
Quick Links


